What Is Saffron? Unraveling Its Detail And Origin
Saffron is a spice used for centuries due to its valuable flavour and numerous health benefits. It is also one of the most expensive spices in the world, with a price tag to match.
This article will explore what Saffron is, how it is grown, its origins and history, medicinal properties, uses and today’s challenges and opportunities. We will also discuss where Saffron comes from and how much it costs.
By understanding the history of Saffron, we can gain insight into its use as an essential ingredient in many cultures worldwide. Saffron has a long-standing place in many cuisines across the globe, from India to Europe to West Asia. Its unique flavour has made it a popular culinary choice for centuries. Still, its many medicinal benefits have only recently been explored more fully.
What is Saffron?

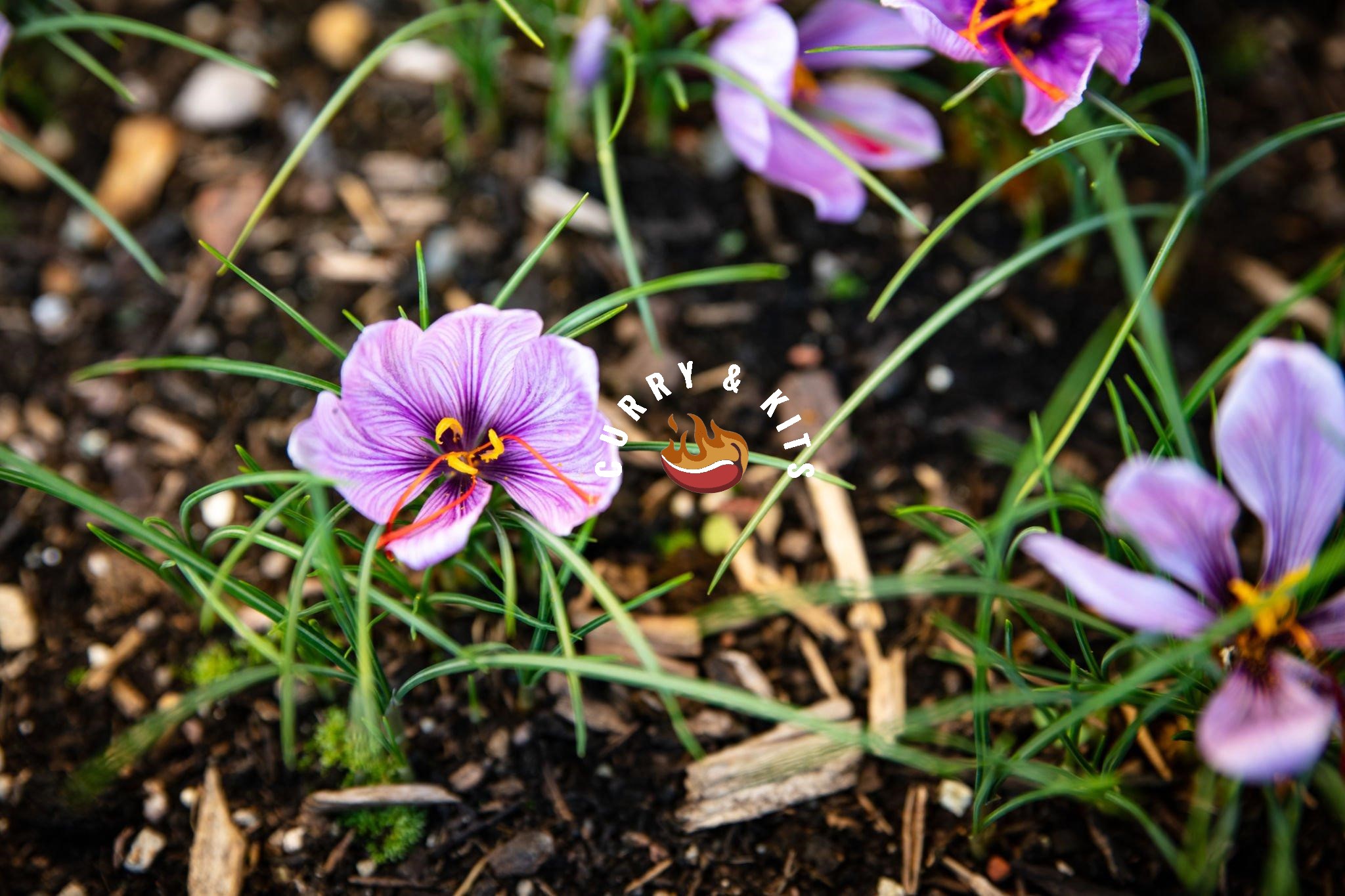
Saffron is a spice derived from the Crocus sativus flower, renowned for its distinct flavour and colour, which has origins dating back to antiquity.
It is believed that the domesticated saffron crocus originated in Iran. However, Greece and Mesopotamia have also been suggested as possible regions of origin.
The vivid crimson stigma and styles, called threads, are collected and dried for culinary purposes. It is known for its subtle aroma and luxurious taste, with a slightly sweet flavour profile.
Saffron’s uses range from seasoning to colouring food items and drinks. Its popularity has endured over time due to its unique properties, making it an essential ingredient in many dishes worldwide.
How to grow Saffron?

Growing Saffron requires specific conditions, making it necessary to follow certain steps for successful cultivation.
The area should be well-drained with plenty of direct sunlight, and the soil should be amended with compost before planting corms 2 inches deep.
Watering is essential but must be done carefully to avoid waterlogging the soil.
Fertilization is not required but may provide healthier plants.
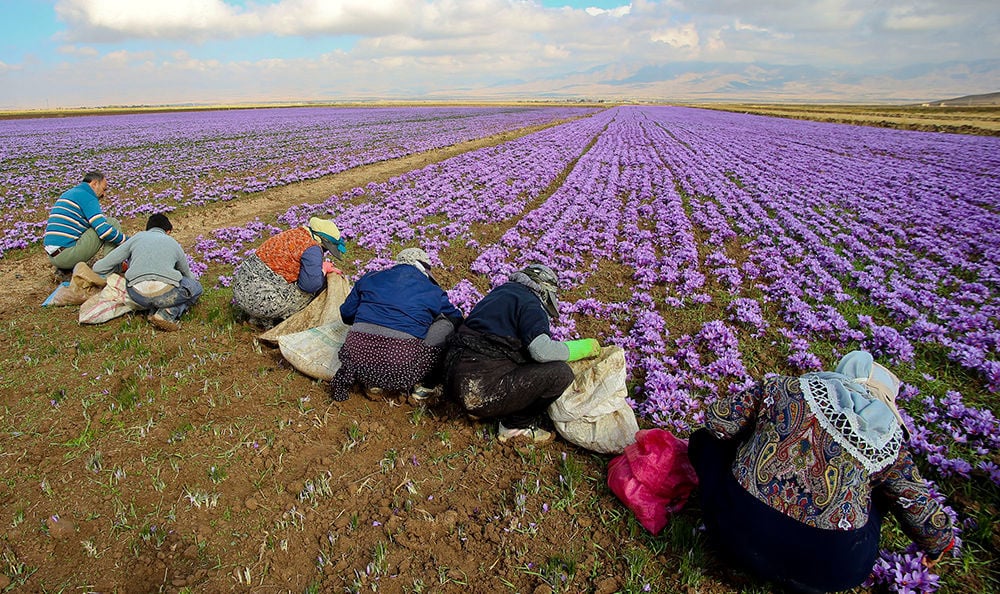
When mature, each flower produces three stigmas which must be handpicked from each flower, spread on trays and dried over charcoal fires for use in food flavouring and colouring.
It can take up to three years for the corms to produce Saffron.
Where does Saffron come from? The Origins of Saffron

Tracing back through the centuries, it is clear that Saffron has significantly impacted many cultures and civilizations across the globe. Its origin is believed to be in Iran. However, Greece and Mesopotamia have also been suggested as possible regions of origin.
‘saffron’ derives from the Latin word ‘Safranum’; its Persian name translates to ‘yellow’. Ancient Persia was well-known for cultivating Saffron for various purposes, such as ritual offerings and healing properties. Domestication of Crocus cartwrightianus (wild Saffron) in Greece during the Bronze Age further propagated this spice’s use throughout Europe.
Today, Iran accounts for 85 per cent of world production due to its favourable climate conditions and generations of farming knowledge.
Saffron in Ancient History

From the Bronze Age to the present day, Saffron has been an integral part of many ancient cultures and civilizations, with its use spanning a variety of purposes.
In Persia, it was cultivated in the 10th century BC and used as a ritual offering.
Ancient Greeks used it as a perfume or deodorizer, while the Romans scattered it about public spaces.
Egyptians associated Saffron with Pharaohs and believed it had healing properties.
Hindus associated Saffron with Lord Vishnu and used it in religious ceremonies.
Persian mythology states that Saffron originated from the tears of Kaveh, who led an uprising against an evil king.
Greek mythology claimed that Hermes first used Saffron to cure his injuries, while Aphrodite used it for beauty enhancement.
Overall, Saffron is known for its long-standing history throughout different societies. It continues to be held in high regard due to its versatility and symbolism within these cultures.
Saffron’s Journey along the Silk Road
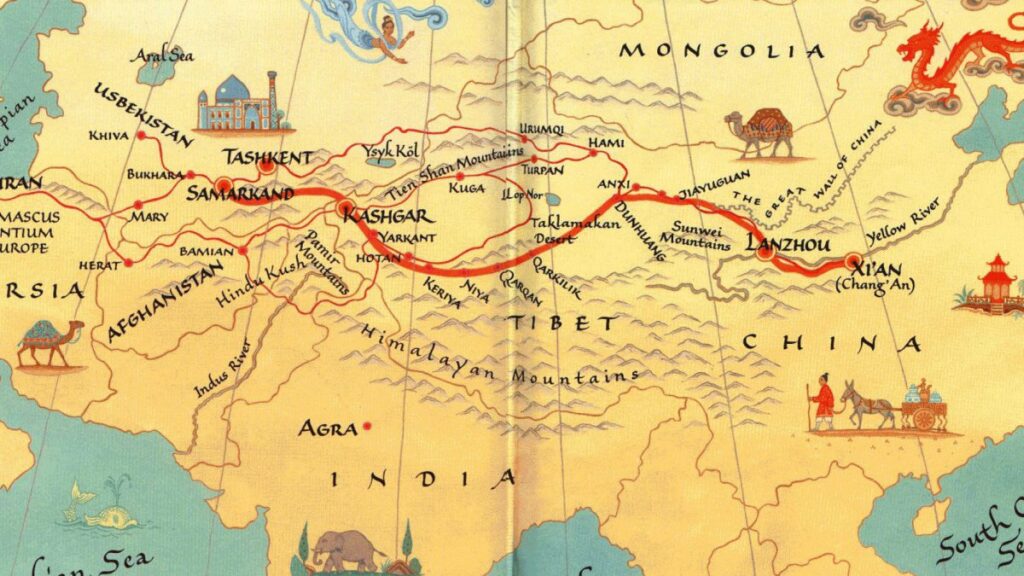
The journey of Saffron along the Silk Road is a captivating tale of trade and exploration that has spanned centuries. It was used as an essential commodity to be exchanged between countries, with merchants travelling from China to India and the Mediterranean regions searching for it.
Saffron’s culinary uses are evident in many cuisines, including Persian, Indian, and Chinese. Additionally, traditional Chinese medicine uses its cooling properties to treat various ailments.
Today, Saffron is still grown and traded in many countries along the Silk Road, such as Iran, India, and China. The brand Saffron Road’ celebrates this journey by offering halal-certified foods inspired by these cuisines. This illustrates how Saffron plays a significant role even after centuries of trading along the Silk Road.
Saffron in Medieval and Renaissance Europe

Exploring the role of Saffron in Medieval and Renaissance Europe reveals its importance as a precious commodity. Initially from the Near and Middle East, it was known to the Greeks and Romans and was introduced to Spain by the Arabs in the 10th century. By this time, it had become a prized spice used for culinary purposes such as seasoning dishes like saffron, rice or chicken, dyeing fabrics, flavouring desserts, and medicinal uses such as cooling the body.
It was expensive and difficult to obtain due to limited production at Saffron Walden in Essex until the 18th century, making it a symbol of wealth among the nobility. Despite its scarcity, it remains an essential part of European cuisine.
What does Saffron taste like

Saffron has a complex and unique flavour profile, with notes of sweetness, floral undertones, earthiness, and nuances that make it an exciting addition to many dishes. Its distinct taste can be described as:
- Semi-sweet and honey-like
- Musky or mushroomy
- Bitter for some
The aroma of Saffron is fragrant and sweet, like honey, with floral undertones. It can have a slightly metallic or even plastic-like taste.
Despite this distinctive flavour profile, Saffron is often used in cooking due to its health-promoting properties and ability to lend complexity to dishes. This spice adds depth and nuance, making each dish more unique and flavorful.
Saffron’s Influence on Cuisine

For centuries, Saffron has been used to add depth and complexity to a variety of cuisines around the world. Its influence is prominent in Indian cuisine, where it is used in dishes like biryani, kheer and Saffron rice, and desserts like ras malai and kulfi.
Similarly, Mediterranean cuisine uses saffron for bouillabaisse soup, paella and risotto. Persian cuisine incorporates Saffron into dishes such as saffron chicken and ice cream alongside pastries like baklava and halva.
Spanish cooking also features this spice in paella, arroz con pollo and fabada asturiana. At the same time, its presence is notable in Medieval-Renaissance Europe with its use in rice and chicken dishes and desserts.
Health benefits are attributed to its bioactive compounds, including crocins, picrocrocin and safranal.
What is Saffron good for? Saffron’s Medicinal Properties

Uncovering the medicinal properties of Saffron, research demonstrates its potential to provide antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumour, neuroprotective, mood-boosting, digestive and cardiovascular benefits.
Crocin, crocetin, safranal and kaempferol are plant compounds in Saffron that act as antioxidants to protect cells from oxidative stress and free radicals.
In vitro and in vivo studies have shown it has anti-inflammatory properties, which could reduce inflammation associated with diseases. Additionally, it has been seen to inhibit cancer cell growth while inducing apoptosis.
Its neuroprotective effects include improving cognitive function while protecting against neurodegenerative diseases.
Saffron also exhibits mood-boosting capabilities and is used as a natural sedative and expectorant in Ayurveda for treating mild depression.
Further benefits include digestive support, such as relieving bloating and indigestion, additionally reducing blood pressure while improving lipid profiles for cardiovascular health.
How to use Saffron? Uses of Saffron
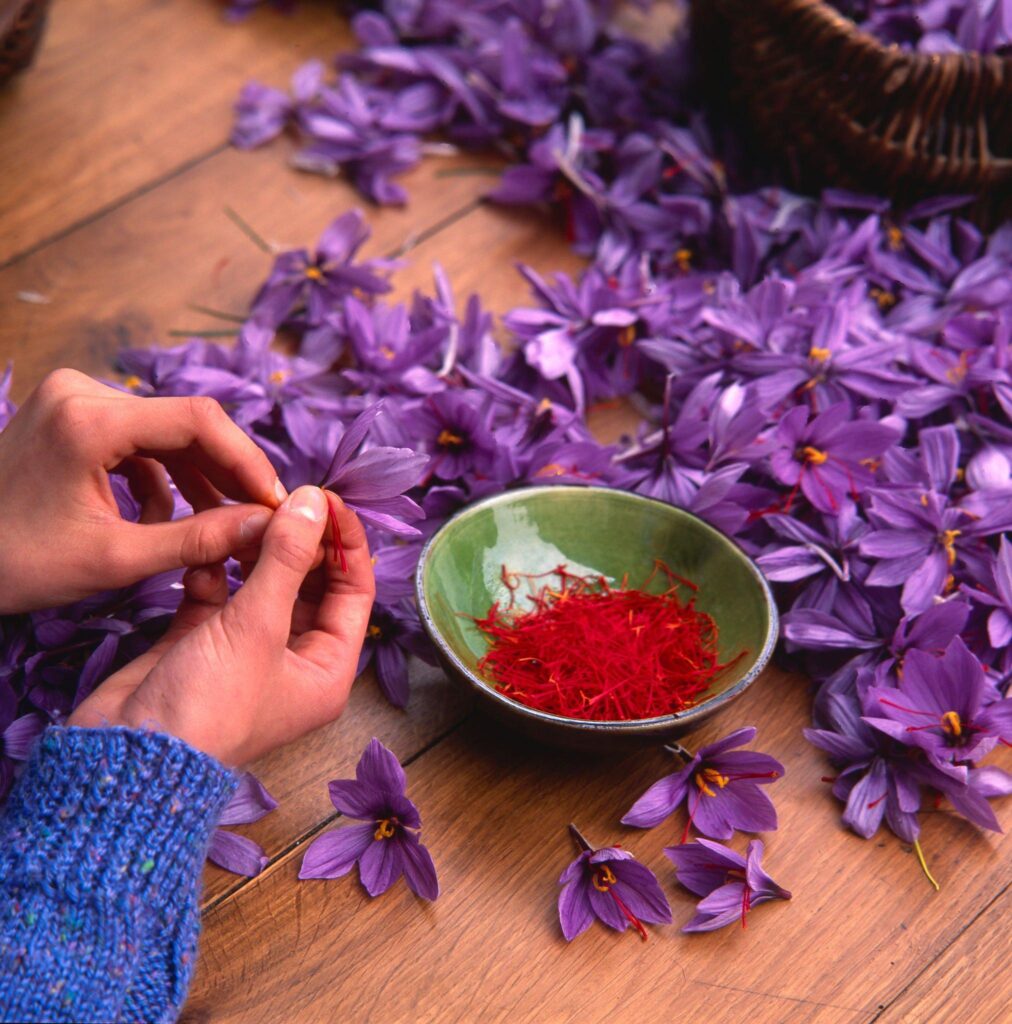

Saffron’s versatility as a spice is showcased through its various uses worldwide, from steeping in water to grinding into a powder and infusing in cooking liquids.
Steeping Saffron in hot water releases its aromatics and gives the liquid a golden hue.
Powdering Saffron can be added directly to rice pilaf, paella, or risotto dishes.
Alternatively, it can be infused into broths, stocks, or milk for an even distribution of flavour and colour throughout the dish.
Only small quantities should be used to avoid overpowering the flavours of a dish with Saffron.
Heat and hydration are also necessary for its flavour release; adding threads alone to salads or roasted vegetables will have little effect.
Therefore, following recipe instructions when using Saffron for optimum results is essential.
How much does Saffron cost?

The cost of Saffron can vary widely depending on the quality, growing conditions, and market demand. The highest grade can go as high as €7 to €9 per gram, while an average pound of Saffron would cost around $5,000. Wholesale prices can be even higher at $10,000 per pound.
Surprisingly, Saffron Imports offers the lowest price at $59.95 per oz for the highest quality worldwide saffron. Despite its exorbitant price tag, Saffron is used sparingly – only a tiny amount is needed to add flavour and aroma to food dishes. This makes it a viable ingredient despite its hefty price tag.
Saffron Today: Challenges and Opportunities
Saffron cultivation today faces several challenges, including climate change, soil-borne diseases, labour shortages, adulteration, and a need for more knowledge about global markets.
Despite these obstacles, there are opportunities for sustainable production through agroforestry and new cultivation methods.
Challenges
Challenges to saffron cultivation include climate change, soil-borne diseases, labour shortages, adulteration, and a need for more knowledge about potential foreign market opportunities.
Climate change affects the quality and quantity of saffron production. Soil-borne diseases can impair growth and yield. The labour-intensive nature of the crop makes it hard to find skilled labourers. Additionally, global markets are flooded with low-quality Saffron due to adulteration, poor packaging, and difficulty in authentication. Lastly, there needs to be more awareness about foreign market opportunities for Saffron and its products.
These issues must be addressed to ensure sustainable production and profitability of saffron cultivation.
Opportunities
Despite the challenges, multiple opportunities for sustainable saffron production can provide economic benefits to farmers and producers.
One approach is agroforestry, which involves growing Saffron with other crops and trees.
Additionally, new cultivation methods under controlled conditions are being studied to increase healthy and disease-free products with the highest quality.
Furthermore, Saffron has been found to have potential health benefits such as treating Alzheimer’s, liver disease, and cancer.
Therefore, Saffron remains a high-value spice providing various economic benefits to farmers and producers.
Conclusion
Saffron is a highly sought-after spice used throughout history and across different cultures. Its unique properties have made it an essential ingredient in traditional medicine, cuisine, and even as a dye.
Growing Saffron requires specific conditions and soil types, making cultivating challenging but rewarding for successful people.
Today, Saffron faces challenges of availability due to its labour-intensive production process and questions of quality control and affordability. However, its unique flavour continues to draw attention from consumers worldwide.
Overall, Saffron remains a fascinating spice with an intriguing origin story and rich cultural significance.






